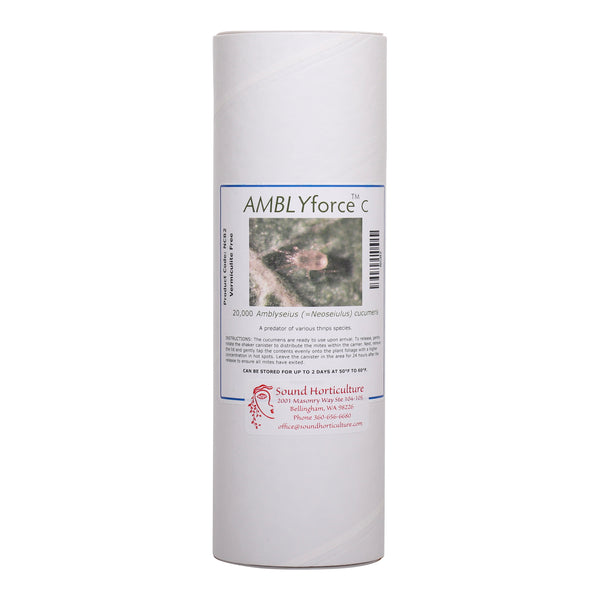
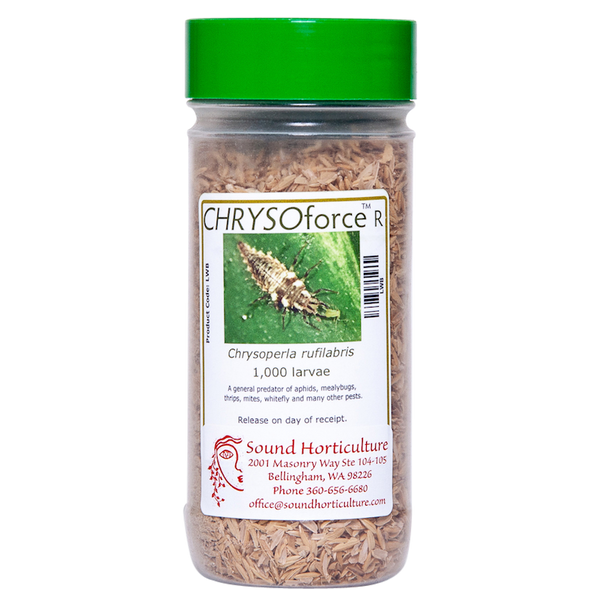
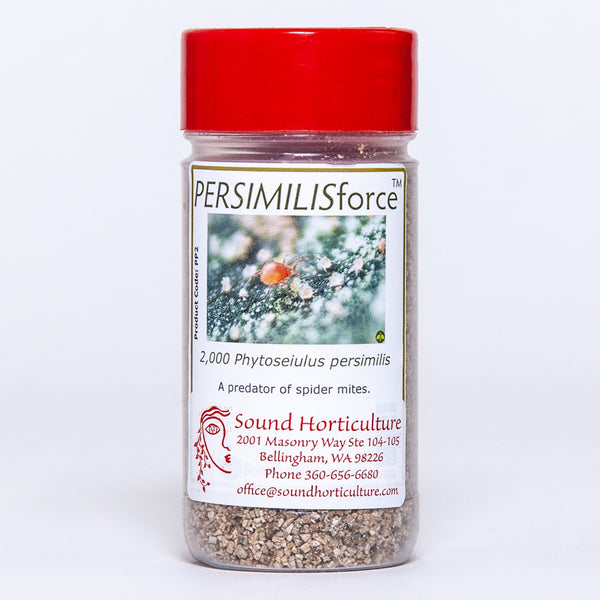
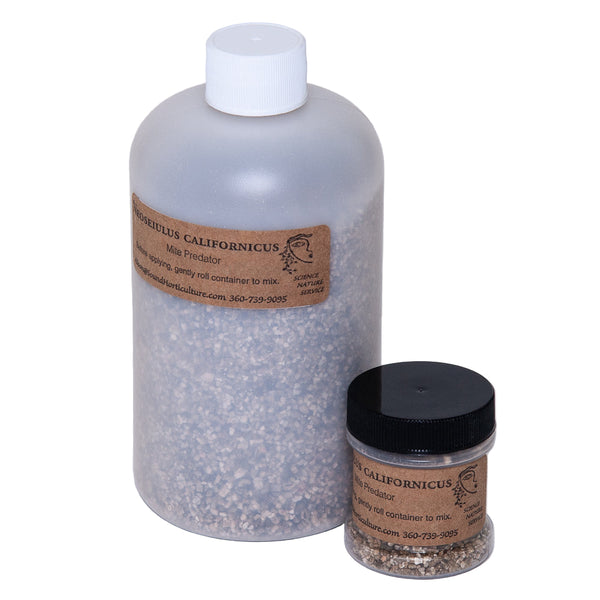
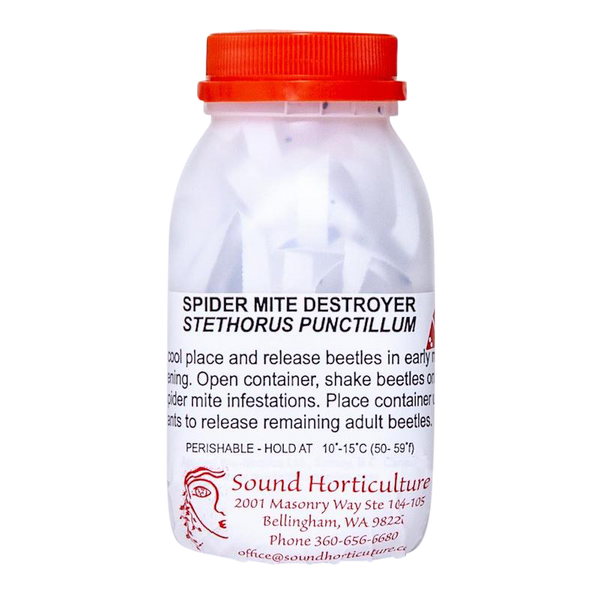
Mite Control
Organic and natural pest control. Mites are tiny pests that feed on a variety of crops causing malformation and distortion of leaves and buds, bronzing and curling. Read more on our Two-Spotted Spider Mite Tech Sheet and Lifestyles of Predatory Mites.
Shop Now for Mite Control
Availability
Price
- 1
- 2